Agents that can live in your body live everywhere. In the air, on a dust particles food and plants; on or in animals and humans; In soil and water, and or virtually every other surface. The range from microscopic organism to large parasites.
The vast majority of these organism do not produce disease, but some do. The majority is usually kept under control by your immune system, but if the system becomes weakened or your encounter an organism to which you have not built up a resistance illness result.
The following are the basic types of organism that cause infectious diseases.
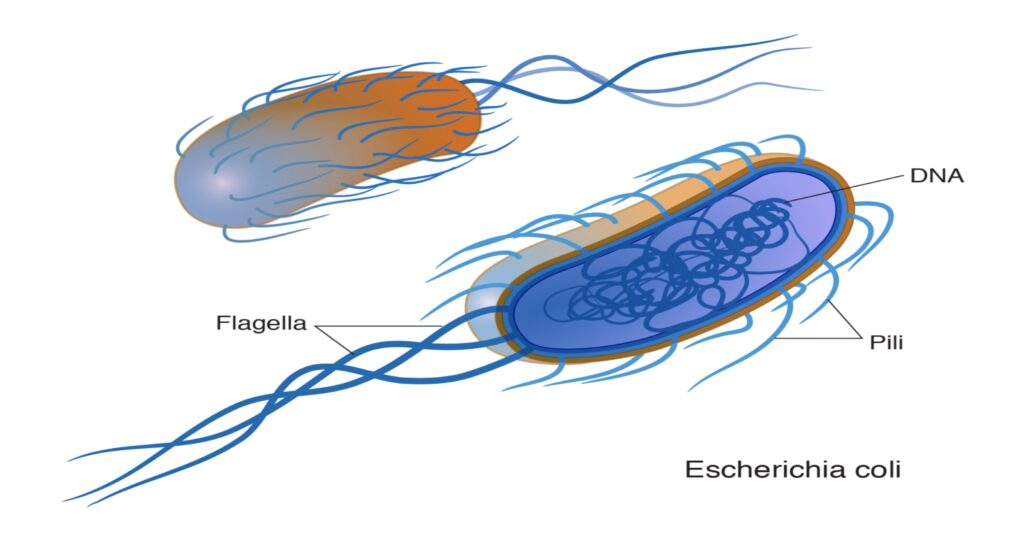
BACTERIA – Bacteria are one-cell organism that are visible only under microscope, they appear as slender rods of groups of round cells, lives without need for other organism, and are able to live and multiply by subdivision. When infectious bacteria gain entry to your body, they multiply and may produce powerful chemicals, called toxins, that damage specific cells in the tissue they have invaded and that cause you to become ill. A few of the more common groups of bacteria that cause disease are staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia, haemophilus, gonococci, rickettsia.
Bacterial Infections
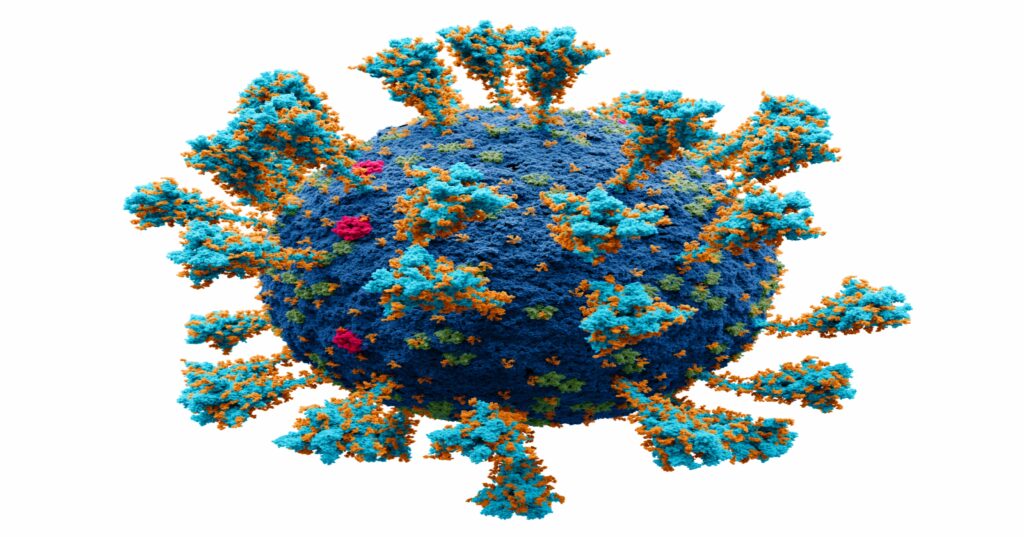
VIRUSES – A virus is not able to reproduce on its own. In its simplest form, it is a capsule containing genetic material. When its invades your body, its enters some of your cells and takes them over, instruction these host cells to manufactures that parts the virus needs in order to multiply. In the process, the host cell eventually is destroyed. Polio, AIDS, and the common cold are among the many ailments cause by viruses.
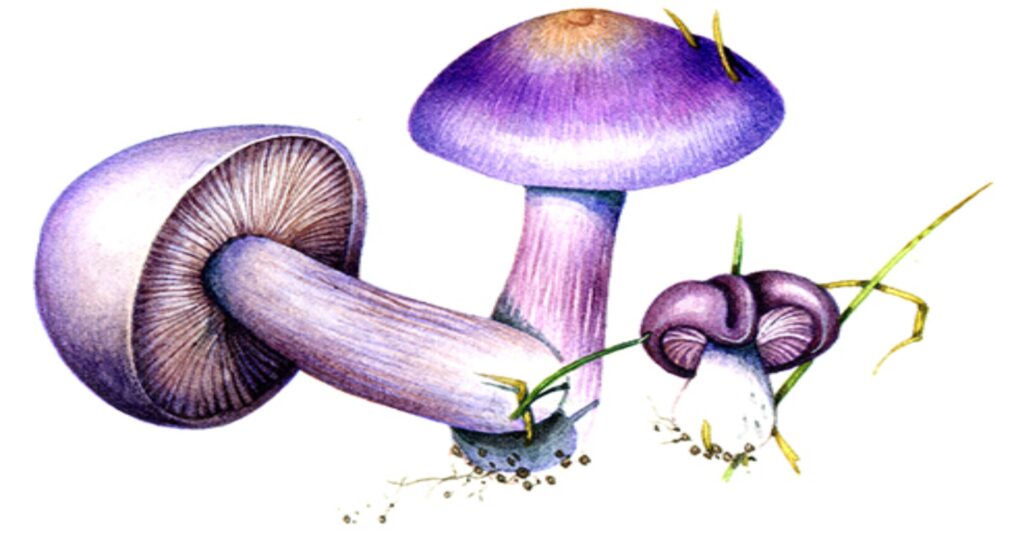

FUNGI – Molds, yeast, and mushrooms all are types of fungi, Obviously, mushrooms are not infectious. But certain yeast and molds can be. These single-cell organism are slightly larger than bacteria of the thousands that are harmless or even helpful (Yeast cause bread to rise) only about 100 cause disease. Candida is one example. It can produce thrush, an infection of the mouth and throat, in infants or in person who have received antibiotic or have impaired immunity.
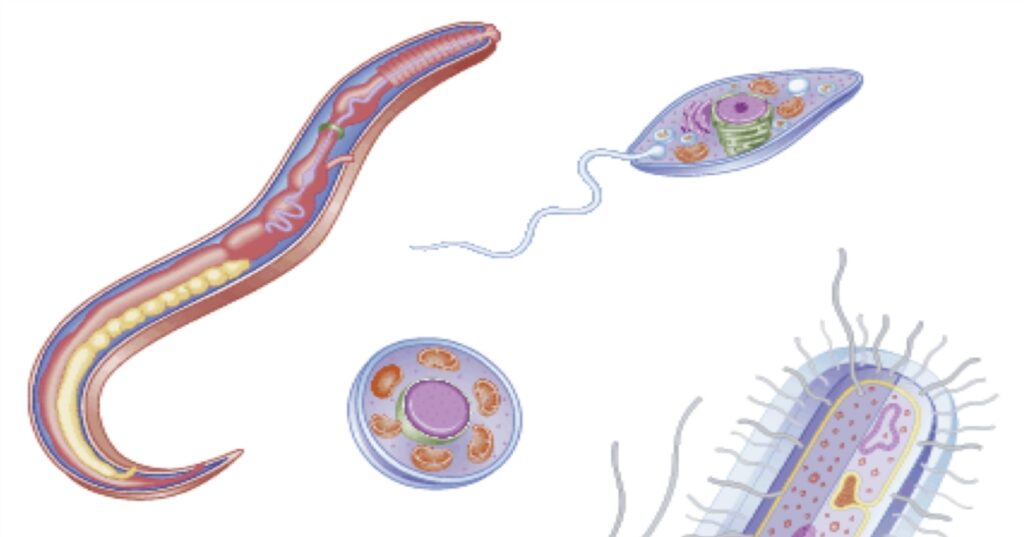
PROTOZOA – Protozoa are a single-cell organism that may live within you as parasite often these organisms spend part of their life cycle outside of humans, living in food, soil, water, or even insects. The Protozoa that cause malaria are example. Many protozoa reside in the intestinal track are harmless although some may cause disease.
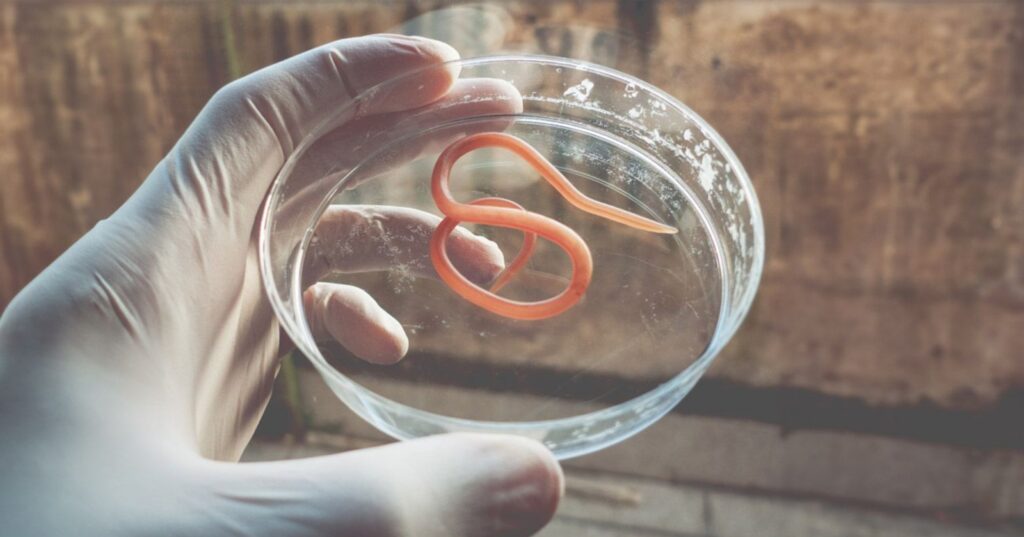

HILMINTHS – The word Hilminth come from the Greek word meaning worm – these are the larger parasites. If they enter your body, they take up residence in your intestinal track, lungs, liver, skin, or even brain when they live off the nutrients in your body. The most common helminths are the tapeworms and roundworms.

