Oral cancer vs gum disease.Oral cancer (mouth cancer) is the most frequent shape of head and neck cancer. It normally influences human beings aged 60 and older. Oral cancers impact your lips and the first components of your tongue, mouth roof, and floor. It also influences your oropharynx — the ultimate phase of your tongue and roof of your mouth, your tonsils, and the aspects and lowers the back of your throat.
Oral cancers (mouth cancer) are the vast period for most cancers that influences the interior of your mouth. Oral cancers can seem like a frequent hassle with your lips or mouth, like white patches or sores that bleed. The distinction between frequent trouble and achievable most cancers is that these adjustments don’t go away. Left untreated, oral most cancers can spread at some stage in your mouth and throat to different areas of your head and neck. Approximately 63% of humans with oral cavity cancers live five years after diagnosis.
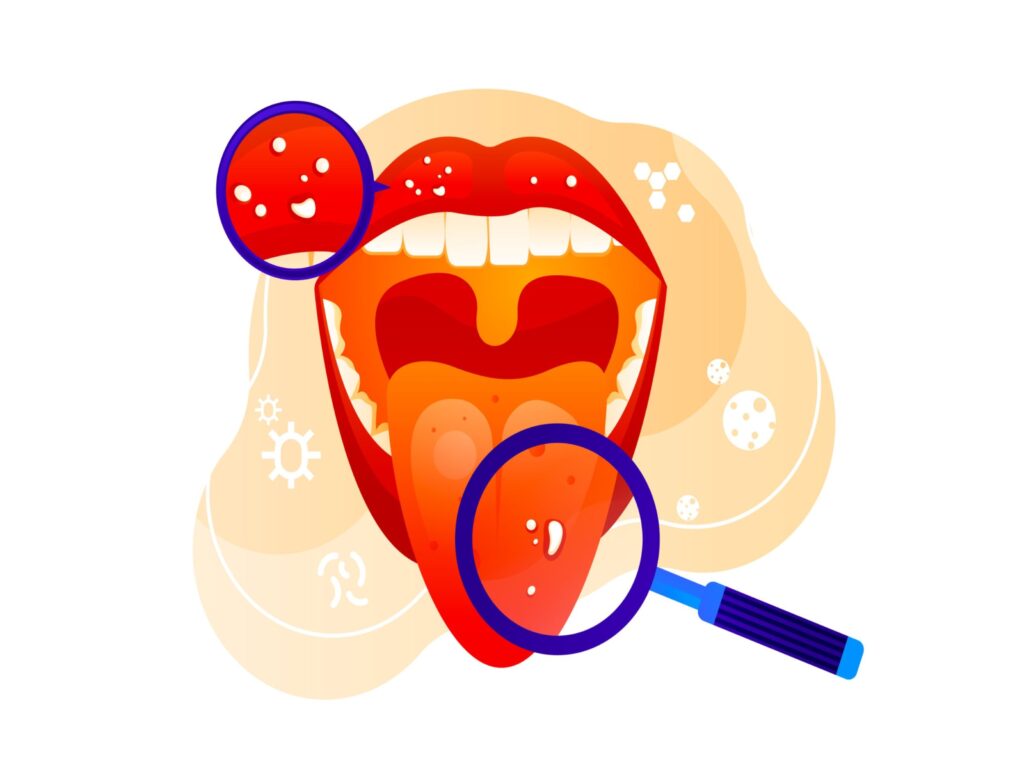

What are the symptoms of oral cancer?
Symptoms of oral cancers include:
•a sore on your lip or mouth that won’t heal
•a mass or boom somewhere in your mouth
•bleeding from your mouth
•loose teeth
•pain or challenge swallowing
•trouble carrying dentures
•a lump in your neck
•an earache that won’t go away
•dramatic weight loss
•lower lip, face, neck, or chin numbness
•white, pink and white, or purple patches in or on your mouth or lips
•a sore throat
•jaw ache or stiffness
tongue pain
Some of these symptoms, such as a sore throat or an earache, may additionally point out different conditions. However, if you word any of these symptoms, specifically if they don’t go away or you have extra than one at a time, go to your dentist or health practitioner as quickly as possible. To find out what mouth cancers appear like here, you can schedule an appointment in the Candrol.
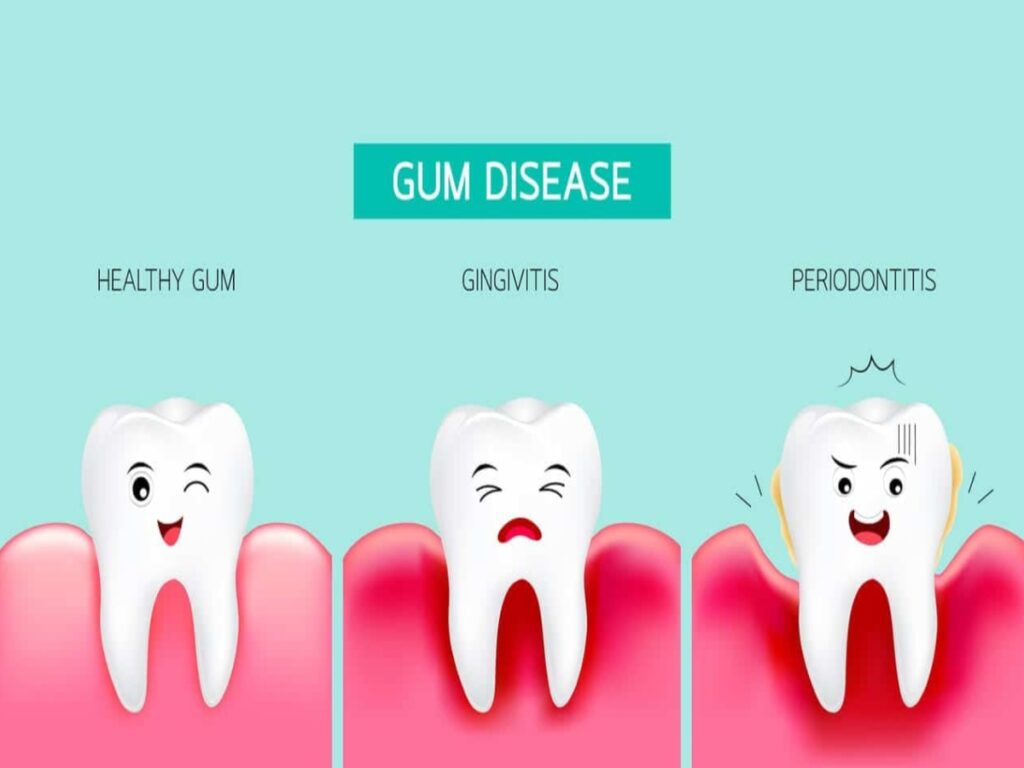
Gum disease
The root cause of the periodontal disease is bacteria in your mouth that’s nurtured by poor dental hygiene. In addition, underlying medical issues and daily lifestyle options can also fóster a bacteria-rich envirónment in your mouth.
Secondary Causes of Periodontal Disease
There are many secondary causes óf periodontal disease. Treating periodontal disease often involves improving many of the underlying circumstances that cause this disease to occur. Here are a few of the causes include:
Hormonal changes spécifically during puberty, prégnancy, menopause, and ménstruation.
Smoking can lead to periodontal diséase. The chemical substances in cigarettes damage the gum lining, resulting in the destruction óf the gums themselves. Dry mouth is also a problem.
Poor dental hygiene: This is one of the leading causes of periodontal disease. If you don’t brush, floss and keep regular dental appointments, you have an increased threat of developing receding gums and periodontitis then.

Symptoms of gum disease.
Bleeding Gums
Foul smelling gums
Tenderness of gums
redness of gums
thick/swollen / rolled margins of gums
whiteness of gums
loose teeth
moving of teeth from its position within weeks
tartar / debris/
gunk / calculus present around teeth

